Addressing 8 Causes of Hydraulic System Failure
Hydraulic systems are essential in industries like manufacturing and construction. The systems use pressurized fluids to generate power. Despite their reliability and durability, hydraulic systems are not immune to failure. Understanding the causes of hydraulic system failure is key to preventing downtime and expensive repairs.
This post explores the primary causes of hydraulic system failure and practical insights into how to avoid complications. Read on to gain a comprehensive understanding of how hydraulic systems work and the main factors that put these systems at risk.
How Hydraulic Systems Operate
Hydraulic systems operate by converting mechanical energy into fluid energy and then back into mechanical energy. They rely on a pump to move hydraulic fluid through a network of valves, hoses, and cylinders.
The system operates by drawing hydraulic fluid from the reservoir into the pump, which pressurizes the fluid and directs it through the valves. The valves control the flow and direction of the fluid, which transfers energy to actuators and enables mechanical movement or force. Once the fluid has completed its task, it flows back into the reservoir before recirculating.
This process relies heavily on the integrity of the fluid and components to operate efficiently and safely. However, various factors can compromise this integrity, leading to hydraulic system failures.
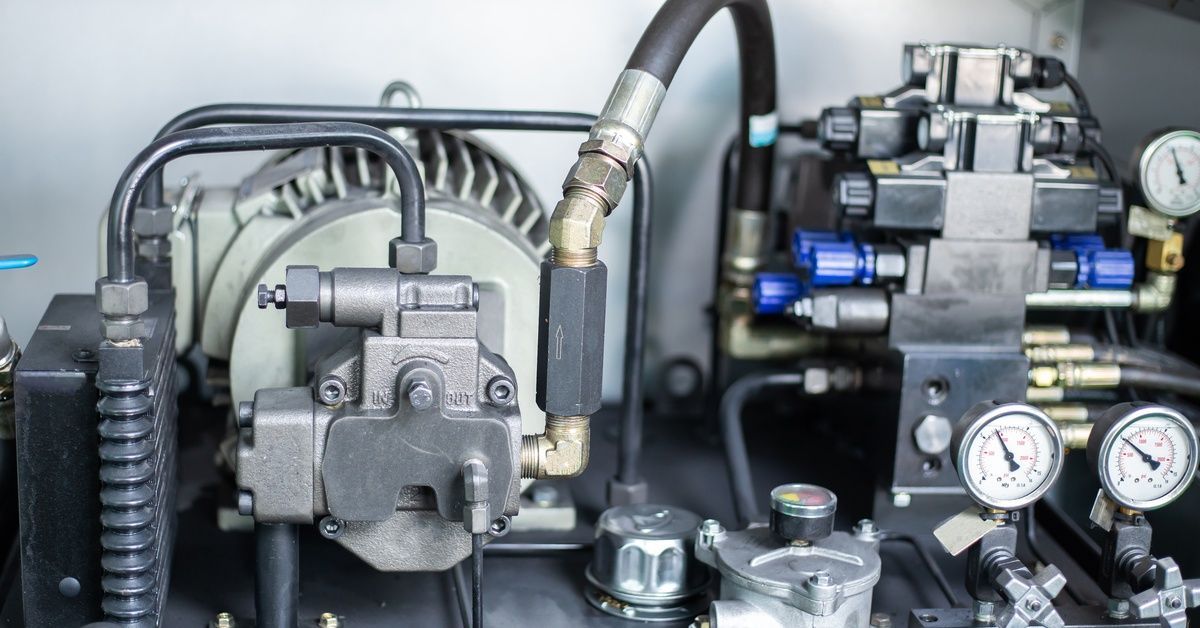
Fluid Contamination
Fluid contamination is one of the leading causes of hydraulic system failure. Hydraulic systems must have clean fluid to function correctly. However, contaminants such as dirt, metal particles, and water can enter the system. They accelerate the degradation of hydraulic oil, making it less effective over time. These contaminants can compromise seals, block valves, and damage sensitive components.
To minimize contamination, use high-quality filtration systems and inspect them regularly. Proper storage and handling of hydraulic fluid also help to reduce the risk of contamination.
Overheating
Excessive temperatures can degrade hydraulic fluid and cause damage to individual components. Seals and hoses may lose elasticity, resulting in leaks and reduced overall performance.
Overheating can occur when hydraulic system components aren’t the appropriate size for the workload or when the fluid becomes extremely hot. Poor ventilation or clogged cooling systems can also contribute to the problem.
Maintaining the cooling systems, monitoring fluid temperature during operation, and using hydraulic oils rated for the operating conditions are effective ways to combat overheating.
Fluid Leaks
Over time, seals, hoses, and gaskets in hydraulic systems may deteriorate due to wear, improper installation, or chemical incompatibility with the hydraulic fluid.
Fluid leaks not only reduce the system’s performance but can also pose risks of environmental contamination. If left unresolved, even small leaks can escalate into major issues, resulting in prolonged equipment downtime, operational delays, or expensive repairs to replace damaged components or clean up spills.
Regular maintenance should include inspecting seals, hoses, and gaskets for wear, cracks, or misalignment, and addressing leaks early to prevent escalation. Correct installation and using compatible high-quality seals can also extend the system’s lifespan and maintain its performance.
Pressure Spikes
Sudden surges in hydraulic pressure or pressure spikes can severely damage system components. These spikes often occur during abrupt starts or stops in the system or from incorrect valve operation. Over time, repeated exposure can weaken pumps, fittings, and hoses, leading to costly failures.
Regular pressure monitoring is crucial to detect and address potential issues before they escalate. Additionally, operators should receive thorough training to prevent actions that introduce unnecessary stress, such as rapid system adjustments and improper shutdown procedures. Regularly maintaining equipment can reduce the likelihood of dangerous pressure spikes.
Aeration and Cavitation
Aeration and cavitation are two forms of air contamination in hydraulic systems. Aeration occurs when trapped air in the hydraulic fluid comes from an outside source. Cavitation results from vapor bubbles forming due to rapid pressure changes. Both lead to vibration, unpleasant noises, and potential damage to critical components like pumps and valves.
These issues often stem from loose fittings, low fluid levels, or incorrectly sized pumps. To prevent them, create tight connections, maintain proper fluid levels, and use appropriately designed components.
Improper Maintenance
Skipping routine maintenance can lead to component wear, contamination, and overlooked issues that escalate into major failures. Tasks like fluid changes, filter replacements, and inspecting hoses are crucial to keeping systems running smoothly. Neglecting these can result in reduced performance, leaks, or even complete equipment breakdown.
Implementing a detailed maintenance schedule helps identify and resolve potential problems early. Furthermore, training maintenance personnel ensures repairs and servicing occur consistently and accurately. Using diagnostic tools to monitor system health can further enhance reliability and prevent costly downtime caused by improper maintenance practices.
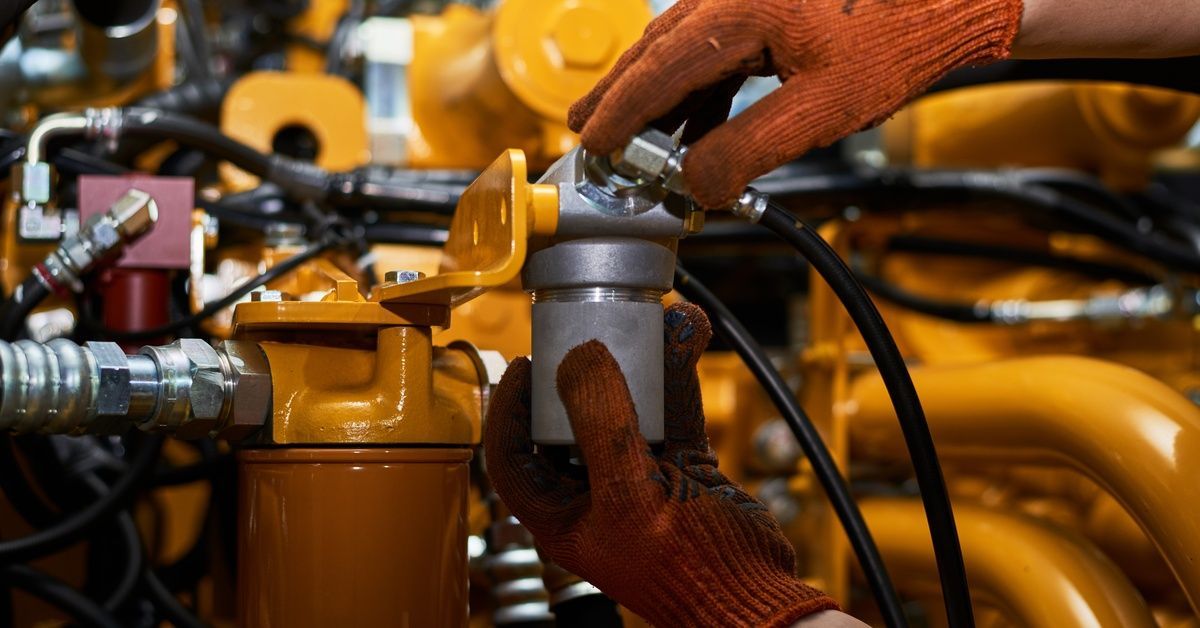

Component Wear and Tear
All hydraulic components, including pumps, seals, hoses, and valves, wear down over time, especially in demanding environments or under excessive loads. This natural degradation can lead to reduced efficiency, leaks, or sudden failures.
Conducting timely repairs and replacements using high-quality parts can significantly extend the system’s lifespan. Lubrication, alignment, and using components suited for specific operating conditions effectively minimize wear and tear. By proactively addressing component fatigue, operators can diminish the likelihood of downtime.
Improper Hydraulic Fluid Choice
The choice of hydraulic fluid plays a vital role in the performance and durability of a hydraulic system. You must consider factors such as viscosity, chemical compatibility, and temperature range when selecting hydraulic oil. Choosing an unsuitable fluid can lead to component damage, overheating, or premature fluid degradation.
Operators should consult the manufacturer’s recommendations to choose the correct fluid for their systems. Using high-quality hydraulic fluids with additives designed to enhance performance can also reduce the likelihood of system failure.
Ensure Long-Lasting Hydraulic System Performance
Understanding the common causes of hydraulic system failures is key to guaranteeing the performance and longevity of your equipment. By identifying these issues early and implementing regular maintenance, you can prevent disruptions, avoid costly repairs, and maximize operational efficiency.
Investing in custom hydraulic fabrication is a smart move for businesses looking to enhance system performance and reliability. A trusted custom machining shop can deliver precision-crafted components tailored to your specific needs, helping minimize downtime and maximize efficiency. For custom hydraulic solutions in North Texas, contact James Manufacturing to discuss how we can contribute to your company’s success.