Differences Between CNC Machining vs. Additive Manufacturing
Manufacturing technologies have come a long way since their inception, with an array of tools and methods now available to produce parts and products. Two of the most well-known and widely used methods are CNC machining and additive manufacturing. While they serve similar purposes, these technologies are fundamentally different in their processes, strengths, and applications.
You’re in the right place if you’re curious about how these methods work and want to understand which one might be better for your industry or project. This guide will explore the fundamental differences between CNC machining and additive manufacturing, comparing their processes, capabilities, and practical applications across industries. With this knowledge, you should have no trouble deciding which is better for your needs.
Understanding CNC Machining
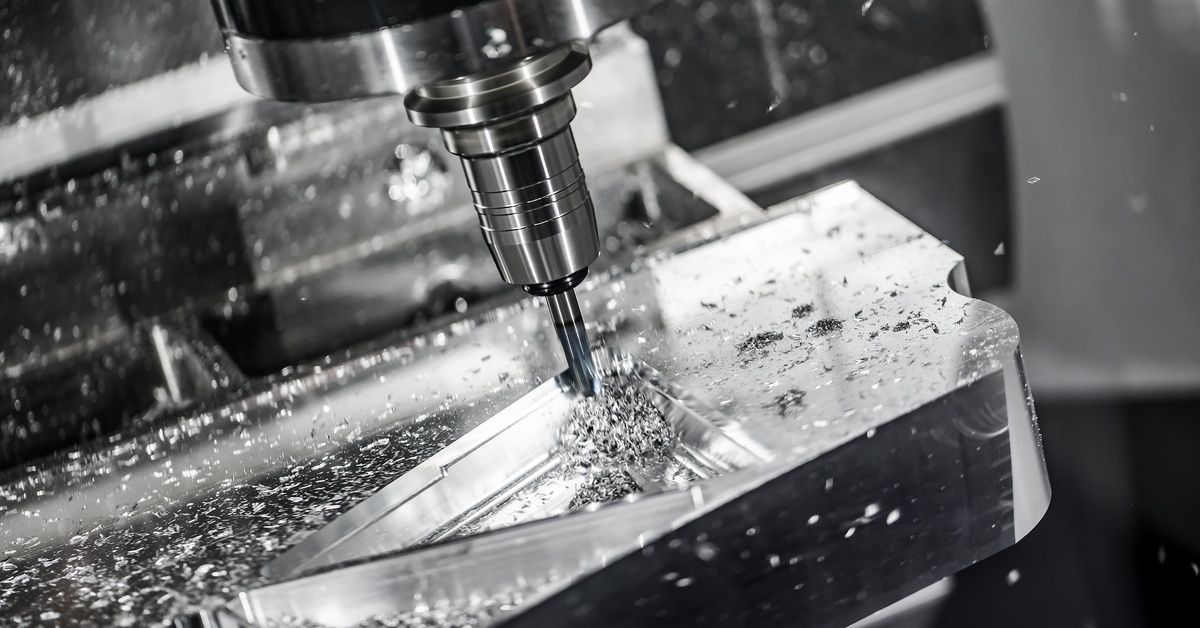
Computer Numerical Control machining, or CNC machining, is a subtractive manufacturing process. Precise computer instructions drive this process, controlling the movement of the cutting tools and workpiece.
How CNC Machining Works
The CNC machining process begins with a digital Computer-Aided Design (CAD) model of the desired part. Technicians convert this model into machine-readable G-code, which directs how the machine cuts, drills, or mills the material.
CNC machines are incredibly versatile and can work with metals, plastics, wood, and even composites.
Applications of CNC Machining
CNC machining excels in industries where precision and durability are critical. Technicians commonly use CNC machining for:
- Automotive parts manufacturing
- Aerospace applications
- Medical devices and implants
- Industrial machinery components
Advantages of CNC Machining
- Machines can produce parts with incredibly high precision and tight tolerances.
- Works well with robust materials such as aluminum, steel, and titanium.
- Ideal for scalable, high-volume production runs.
Limitations of CNC Machining
- The subtractive nature leads to material waste.
- Some complex geometric designs aren’t feasible without advanced tools.
- Initial setup and material costs can be high for small runs.
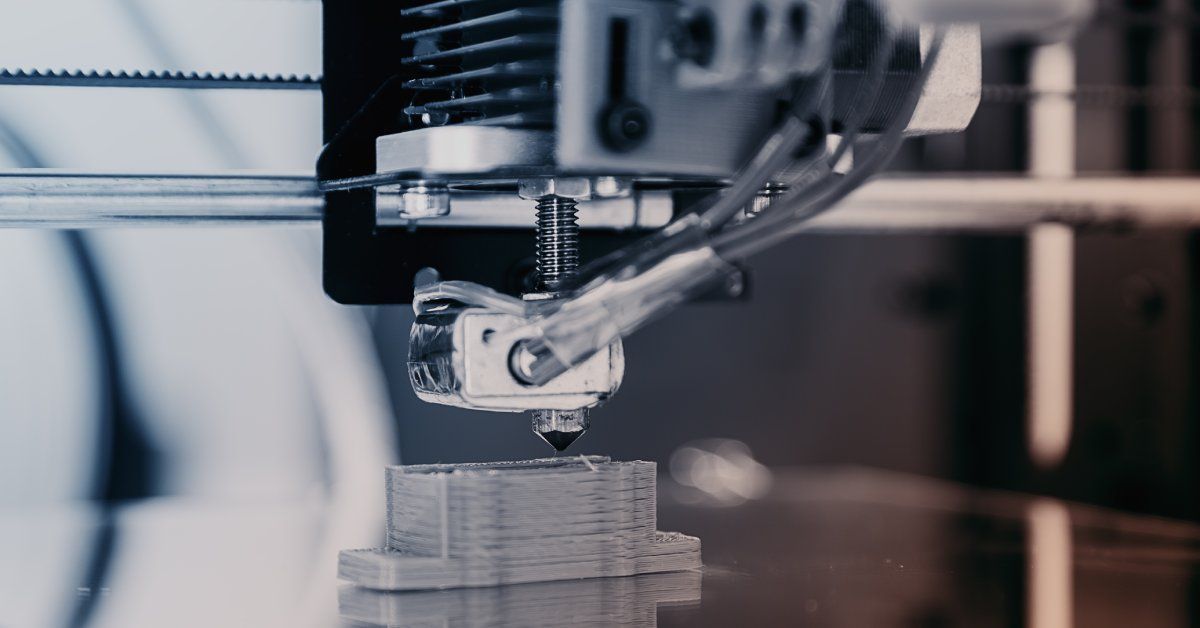
Understanding Additive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing, often referred to as 3D printing, is a fundamentally different process. Instead of cutting material away, it builds objects layer by layer, directly from a digital model.
How Additive Manufacturing Works
The process begins with a CAD model of the desired part, just like CNC machining. Technicians then use the machine to slice the model into thin digital layers. A 3D printer follows these instructions to deposit material one layer at a time until the object is complete. Designs often employ materials such as plastic, resin, metal powder, or even biocompatible substances.
Applications of Additive Manufacturing
Many industries use additive manufacturing, benefiting from its customization and design complexity. These industries use it for processes such as:
- Rapid prototyping
- Custom medical prosthetics
- Jewelry design
- Complex aerospace and automotive parts
Advantages of Additive Manufacturing
- Allows for design flexibility, the creation of intricate geometries, lightweight structures, and unique designs.
- The machine only produces the material required for the product, reducing waste.
- Technicians can iterate more quickly, developing and testing prototypes rapidly.
Limitations of Additive Manufacturing
- The range of usable materials is growing but is still somewhat limited compared to CNC machining.
- Currently, it’s slower than CNC machining for high-volume production.
- Parts may require additional post-processing for a smooth finish.
By getting to know the strengths and weaknesses of each approach, you can ensure your manufacturing process is efficient and budget-friendly.

Key Differences Between CNC Machining and Additive Manufacturing
CNC machining and additive manufacturing can help organizations achieve the results they want with minimal effort. Here are some of the fundamental differences between the two approaches.
1. Material Usage and Waste
- CNC machining is a subtractive process that produces significant material waste, particularly for complex designs.
- Additive manufacturing utilizes only as much material as necessary, significantly reducing waste.
2. Production Speed and Volume
- CNC machining is faster for high-volume production runs and delivers consistent part quality.
- Additive manufacturing excels in single- or low-volume runs but takes longer for larger batches.
3. Design Flexibility and Complexity
- CNC machining is best for designs with simpler geometries. Complex designs may need specialized machines or tools.
- Additive manufacturing is perfect for complex shapes and lightweight, intricate, or hollow designs.
4. Material Options and Strength
- CNC machining can work with a range of durable materials, including metals, plastics, and composites.
- Additive manufacturing is limited to certain materials but has the advantage of creating hollow or lattice-like structures for lighter-weight products.
Consider factors such as design complexity, production volume, material requirements, and budget constraints when deciding which method is best for your project. A combination of both methods may yield the best results in some cases.
Cost Analysis
Manufacturers must factor in the overall costs of each process before deciding which to use. Here are some basic things to consider.
Initial Setup and Production Costs
- CNC machining typically requires a substantial upfront investment in tooling and setup, especially for custom parts.
- Additive manufacturing has minimal setup costs, making it more cost-effective for low-volume or custom products.
Long-term and Customization Costs
- CNC machining has become more cost-effective for large production runs due to its scalability.
- Additive manufacturing offers a financial advantage for highly customized or low-volume projects.
Which Is Cheaper?
CNC machining typically requires higher initial setup costs due to the need for specialized machines, tools, and skilled operators. However, its high production speed and efficiency for large-volume runs can offset these costs. Additive manufacturing becomes more expensive in the long run due to slower print times and material costs, though it may have lower initial setup costs.

Industry Applications
The choice between CNC machining and additive manufacturing largely depends on the specific needs and requirements of each industry. Here are some common applications for both methods across various sectors:
CNC Machining
- Produces durable automotive components and gearboxes.
- Crafts high-precision aerospace parts, such as turbine blades.
- Heavy-duty industrial manufacturing equipment parts.
Additive Manufacturing
- Builds custom prosthetics, dental implants, and other health-care related components tailored to individuals.
- Prototypes consumer goods and industrial designs with lightning speed.
- Creates lightweight, intricate airframe components.
CNC machining and additive manufacturing are constantly evolving to meet the demands of these industries as technology continues to advance.
Exploring Future Trends
Emerging technologies in CNC machining, such as multi-axis machining and hybrid machines, are enabling the production of more complex parts with higher precision. Additive manufacturing is evolving with faster printing speeds, expanded material options, and enhanced printers capable of large-scale production. Metal additive manufacturing and other innovations are already bridging the gap between prototyping and end-use parts.
Additionally, hybrid manufacturing systems that combine subtractive and additive methods are becoming available. These machines enable manufacturers to leverage the strengths of both technologies, opening opportunities for even more sophisticated designs.
Choosing the Right Technology for Your Needs
The approach you take to manufacturing depends on your specific project requirements, including material, design complexity, production volume, and budget. By understanding the key differences between CNC machining and additive manufacturing, you can make an informed choice tailored to your unique needs.
Are you ready to take your project ideas to completion? James Manufacturing offers a range of services, including aluminum CNC machining, to help you achieve your vision without breaking the bank. Let’s collaborate and innovate together to discover new growth!